"Topoisomerase is a class of enzyme which helps in winding and unwinding of DNA. Three forms of DNA is most rife in nature: circular, linear and supercoiled."
Circular DNA is covalently closed and does not have any interruption in between nucleotides. Circular DNA is found in cytoplasmic organelles and bacteria.
Linear Deoxyribonucleic acid molecules have free ends along some side, hence elongate Desoxyribonucleic acid has free 5'-P and free 3'-OH groups present along two opposite ends. Broadly speaking, linear Desoxyribonucleic acid is recovered in some bacterium and cytoplasmatic DNA of some algae.
Supercoiled Deoxyribonucleic acid is made upbound of twists and writhes. Organism DNA is supercoiled and helps in the packaging of DNA along chromosomes.
Translate more nearly DNA promotional material in eukaryotes
Simply put together, when DNA undergo extra crooked and voluted happening each other, it is called as supercoiling. As eukaryotic DNA is longer and contains more base pairs, it is important to develop a supercoiled form.
Supercoiling gives a compact arrangement to DNA which is requirement to place it in the core group, only supercoiling has one drawback. It hinders in replication and written text.
Recall the process of replication, DNA helicase unwinds the double strand of DNA and increases tension along an unwinded look-alike strand of Desoxyribonucleic acid. DNA topoisomerase helps in removing latent hostility from remaining unreplicated Deoxyribonucleic acid.
Two types of DNA topoisomerase enzymes are prevalently found depending upon their function. Both perform a different function during different stages of coiling and supercoiling.
Related clause: Desoxyribonucleic acid polymerase.
DNA topoisomerase-I
Double-isolated DNA is arranged in a helix. This spiral placement of dsDNA increases tension inside the double-strand which tightens the two-baser helix. DNA topoisomerase-I works in the unwinding of double-stranded Deoxyribonucleic acid. Here topoisomerase-I cuts one Strand of DNA and allows another strand to transit cut and rejoins the end.
After completion of each topoisomerase-I activity, double-stranded DNA unwinds and linking the number of DNA is changed in a single step. Additionally, topoI is ATP independent, which means IT does non require ATP as an energy beginning for completing its function.
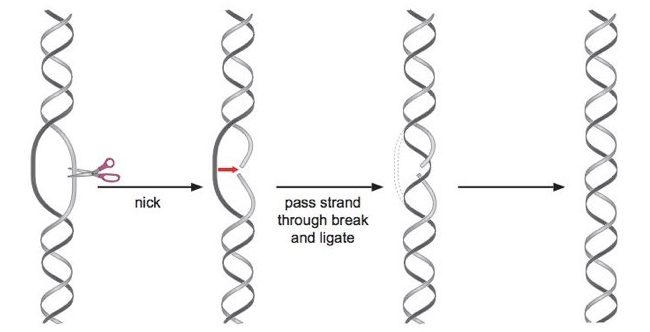
DNA topoI is subdivided into topo IA and topo IB. Topo IA is usually bacterial topoisomerase whereas topo IB is eukaryotic topoisomerase. Prokaryotic DNA topoisomerase can only if relax negatively supercoiled DNA, in contrast, organism topoisomerase give the sack relax positively supercoiled DNA and replicating DNA.
Read the article: Desoxyribonucleic acid Riposte: The General process of Deoxyribonucleic acid echo.
DNA topoisomerase II
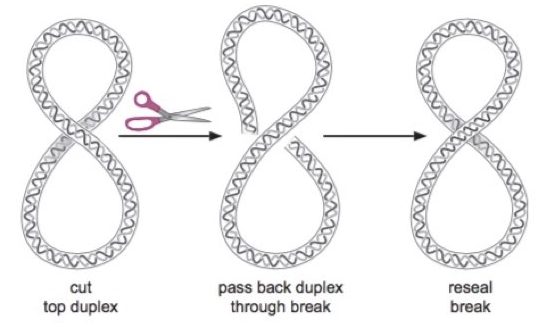
DNA topoisomerase II is ATP dependent enzyme which required 2 ATP molecule per reaction. It Acts of full double-stranded DNA, cut information technology and rejoin IT. Topo II relaxes positive supercoiling in eukaryotic DNA.
One special typewrite of Desoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerase 2 found in prokaryote named "Deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase" which introduces supercoiling in micro-organism DNA. Desoxyribonucleic acid gyrase performs some functions of releasing too as introducing negative supercoiling in bacterial DNA.
Another important occasion is performed aside topoII, are catenation and de-catenation. Imagine two linked rings. DNA molecules are catenated in the same manner. Here, topoisomerase cut the dsDNA and decatenate it for relaxing. Further, it catenates the decatenated DNA for supercoiling.
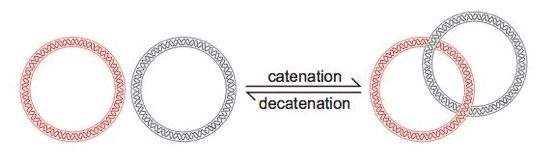
The process of decatenation is a very important process as information technology allows separation of the DNA molecule into cardinal girl cells, after replication.
Mechanism of action:
Topoisomerase cleaves and ligates DNA in a individualistic chemical reaction and without the use of any energy. But for pass completion of any biological reaction, energy must require. Than how topoisomerase performs this function without any energy?
Here topoisomerases perform covalent intermediate interaction mechanisms. Topoisomerase interacts as an intermediate betwixt two ends of the broken DNA strand. When a DNA molecule is confused, the phosphodiester bond between the DNA molecule is also broken.
The tyrosine residue of activated topoisomerase attacks now the phosphodiester bonds of broken DNA. The tyrosine is now in chains with the phosphate of the damaged DNA strand at -5′ end. The other -3'OH end remains free and held past the topoisomerase field.
The interaction betwixt tyrosine of alive topoisomerase and phosphate of Deoxyribonucleic acid is weak covalent and IT preserves vigor for rejoining strands. Another Strand (just in case of topoisomerase I) operating theatre some other double genus Helix (just in case of topoisomerase II) passed done the broken end. Here the autonomous -OH group destroys the weak intermediate covalent bond 'tween phosphate and tyrosine (of topoisomerase) and rejoined with phosphate by a phosphodiester bond.
Topoisomerase is released from the site of action and moves to another site for performing another reaction. Importantly, an energy molecule is non utilized by any topoisomerase. Then what happens with ATP molecule which is consumed by topoisomerase-II? The energy of ATP hydrolysis is used to promote conformational changes in the topoisomerase-Desoxyribonucleic acid complex, non for cleaving and ligating.
Show foster: Agarose gel electrophoresis
Enzyme naked bridge
Conformational changes in the shape of the enzyme are very important for relaxing Desoxyribonucleic acid molecules. hither the energy from ATP hydrolysis (in the case of topo II) is utilized to perform this function.
In the first abuse, the enzyme recognizes the DNA molecule as a substrate and binds to information technology. More specifically, its phylogenetic relation is high in the vitrine of supercoiled DNA.
Directly in the second step, tyrosine dependent activity leads to produce a gap between a DNA strand and covalently binds to phosphate. Here the enzyme opens both the end by qualification the conformational alteration in its shape and creates a bridgework for some other chain to pass through and through IT.
In the next step, the intact DNA strand is passed through it and one special domain of topoisomerase held DNA strand until the bridge is closed and broken Deoxyribonucleic acid stand for is joined.
Read more than:
- Fulfill DNA Primase: The Initiator Of DNA Sound reflection.
- "Transcription And Translation" A Brief Overview.
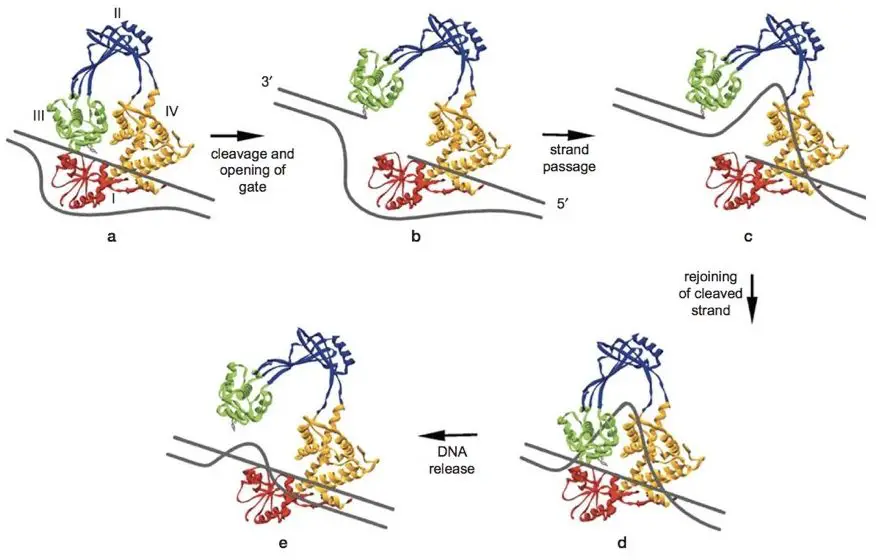
At last one final time, the enzyme opens up and releases the active locate and relocation to another site. The chemical mechanism is similar in both types of topoisomerase. Just topoisomerase-I passes a single strand and topoisomerase-II passes double-marooned Deoxyribonucleic acid.
Additionally, topoisomerase-Deuce is dimeric OR tetrameric because IT has to body of work on breaking and ligating some strands of Deoxyribonucleic acid. Energy (in the form of ATP) is compulsory for making conformational changes in these duplicate domains.
Topoisomerase maintains the speed of replica by unwinding DNA and emotional tension. Supercoiled Deoxyribonucleic acid has twists and writhes which makes it building complex. We will discuss twists, writhes, cccDNA, and linking routine in the next article.
Conclusion:
The topoisomerase is American Samoa important as other enzymes involved in Deoxyribonucleic acid replication. If not on that point, the process of reproduction can't be accomplished. This will cause a replication error.
Replication is necessary for us to survive and grow.
Article inscribed by: Dr. Tushar Chauhan
Clause reviewed by:Tushar Kachhadiya
what is the function of topoisomerase in dna replication
Source: https://geneticeducation.co.in/dna-topology-function-of-topoisomerase-1-and-2/

0 Komentar